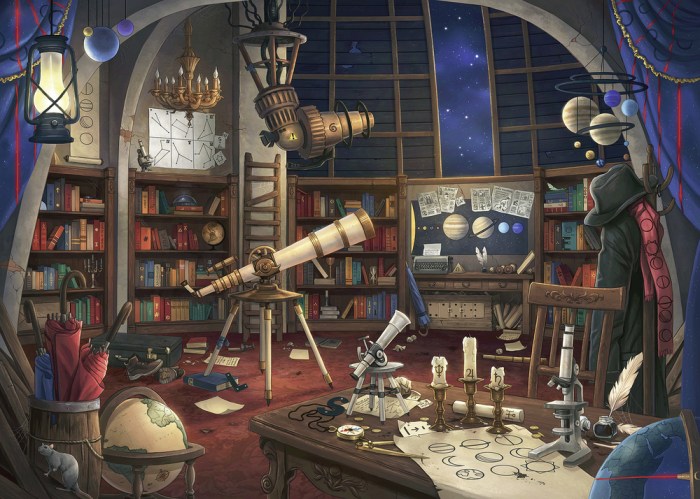
Ever wondered about the ingenious minds behind those thrilling escape rooms? This isn’t just about locks and keys; it’s a blend of creative puzzle design, clever technology integration, and savvy business strategies. We’ll delve into the mechanics of various puzzle types, from classic logic challenges to cutting-edge tech integrations, exploring how designers craft immersive experiences that balance challenge with player enjoyment.
Prepare to unlock the secrets behind the escape room phenomenon!
From the initial spark of an idea to the final marketing push, building a successful escape room involves a multifaceted approach. We’ll examine the design principles that make puzzles both engaging and solvable, explore the role of technology in enhancing the experience, and discuss the crucial business aspects that contribute to a thriving escape room enterprise. Whether you’re a budding game designer, an aspiring entrepreneur, or simply a puzzle enthusiast, this exploration promises a fascinating journey into the world of escape room puzzles.
Escape Room Puzzle Mechanics

Escape rooms thrive on their intricate puzzles, demanding players to combine logic, observation, and teamwork to achieve victory. The success of any escape room hinges on the clever design and execution of its puzzle mechanics. These mechanics dictate the difficulty, player engagement, and overall experience.
The core mechanics of common escape room puzzles often fall into several categories, each presenting unique challenges and rewards. Understanding these categories helps in appreciating the artistry and ingenuity behind the design of these immersive experiences.
Common Escape Room Puzzle Types
Escape rooms utilize a variety of puzzle types to create a multifaceted and engaging experience. Logic puzzles require deductive reasoning and pattern recognition to solve. For example, a sequence puzzle might require players to decipher a numerical or symbolic pattern to unlock a combination lock. Word puzzles, on the other hand, often involve anagrams, ciphers, or riddles that demand linguistic skills.
A classic example would be a Caesar cipher, where each letter is shifted a certain number of places in the alphabet. Code-breaking puzzles can incorporate elements of both logic and cryptography, requiring players to decode messages or symbols to reveal hidden clues. A common example would be a substitution cipher where each letter is replaced by a symbol or another letter.
Innovative Puzzle Mechanics in High-Quality Escape Rooms
High-quality escape rooms often go beyond standard puzzle types, incorporating innovative mechanics to enhance the immersive experience. For example, some rooms utilize augmented reality (AR) technology to overlay digital clues onto the physical environment, blurring the lines between the real and virtual worlds. Imagine a puzzle where players use a tablet to scan a seemingly ordinary painting, revealing a hidden code only visible through the AR application.
Another example is the use of physical contraptions and mechanisms, such as intricate lock systems or moving parts that require manipulation to reveal hidden compartments or solutions. A well-designed physical puzzle might involve a series of gears and levers that must be manipulated in a specific sequence to open a secret passage. These innovative approaches enhance the sense of discovery and immersion, elevating the experience beyond traditional puzzle-solving.
Difficulty Levels and Player Engagement of Different Puzzle Mechanics
The difficulty and player engagement of escape room puzzles vary significantly depending on the chosen mechanics. Logic puzzles, while sometimes challenging, often offer a sense of satisfaction upon solving, particularly for players who enjoy intellectual stimulation. Word puzzles, however, can be more polarizing, with some players finding them engaging and others finding them frustrating. Code-breaking puzzles usually fall on the higher end of the difficulty spectrum, requiring a deeper understanding of cryptography or pattern recognition.
The engagement level is also heavily influenced by the puzzle’s presentation and integration within the overall narrative of the escape room. A well-integrated puzzle, regardless of its inherent difficulty, is more likely to engage players than an isolated or poorly explained one.
A Novel Escape Room Puzzle Mechanic: The Musical Cipher
This puzzle mechanic utilizes musical notation to encode a message. Players are presented with a sheet of musical notation, seemingly random at first glance. However, each note corresponds to a letter of the alphabet based on its position within a specific musical scale (e.g., C major). The rhythm and duration of the notes could add an additional layer of complexity, perhaps indicating spaces between words or specific punctuation.
The solution involves translating the musical notes into their corresponding alphabetical equivalents, revealing a hidden phrase or code that unlocks the next stage of the escape room.
Variations could include using different musical scales, incorporating rests to represent spaces or punctuation, or even introducing rhythmic patterns to represent numbers. The difficulty could be adjusted by changing the complexity of the musical notation or by adding additional layers of encoding. For example, a simpler version might use only quarter notes, while a more difficult version might incorporate dotted notes, triplets, and rests.
This mechanic combines logic, musical knowledge (or the ability to use a reference sheet), and code-breaking elements, offering a unique and potentially engaging challenge for players.
Escape Room Puzzle Design Principles
Crafting truly memorable escape rooms hinges on more than just clever locks and cryptic clues. It’s about weaving together engaging puzzles with a compelling narrative and immersive theme, creating an experience that players will rave about long after they’ve escaped. This involves careful consideration of several key design principles.
Storytelling and Theme Integration
A strong narrative acts as the glue that binds the individual puzzles together, transforming a collection of riddles into a cohesive and captivating experience. The theme should permeate every aspect of the room, from the set design and props to the puzzles themselves. For instance, a pirate-themed escape room might feature puzzles involving decoding nautical charts, deciphering cipher messages written in pirate slang, or even navigating a miniature replica of a ship’s interior.
The puzzles themselves should organically arise from the story, furthering the narrative and enhancing player immersion. Without a strong narrative framework, the puzzles risk feeling disjointed and arbitrary.
Creating Intuitive and Engaging Puzzles
Intuitive puzzle design is paramount. Players should be able to understand the goal of each puzzle relatively quickly, even if the solution requires some creative thinking. This is achieved through clear presentation of the puzzle elements, logical progression of steps, and appropriate feedback mechanisms. Engaging puzzles are those that spark curiosity, challenge players’ problem-solving skills, and provide a sense of accomplishment upon completion.
Consider using a variety of puzzle types to cater to different player strengths and preferences, balancing logic puzzles with word games, observation challenges, and physical manipulations. The use of red herrings, while tempting, should be employed sparingly to avoid undue frustration.
Balancing Difficulty and Player Frustration
The sweet spot in escape room puzzle design lies in finding the right balance between challenge and frustration. Puzzles should be challenging enough to be rewarding but not so difficult as to discourage players. A well-designed puzzle will gradually increase in complexity, providing players with a sense of progression and accomplishment. It’s crucial to test puzzles extensively with diverse groups of players to gauge their difficulty level and identify potential points of frustration.
Providing subtle hints or clues, without explicitly giving away the solution, can help players overcome roadblocks without resorting to outright solutions. For example, a seemingly complex code could be subtly hinted at through a nearby object bearing a similar pattern.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Escape Room Puzzle Design
Designing a successful escape room puzzle involves a methodical approach.
- Concept and Theme Definition: Begin by establishing a clear theme and narrative. What story will your escape room tell? What atmosphere do you want to create?
- Puzzle Brainstorming: Brainstorm several puzzle ideas that align with your theme and narrative. Consider the variety of puzzle types and player skill levels.
- Prototype Development: Create rough prototypes of your chosen puzzles. This could involve sketching designs, creating basic models, or writing out the puzzle mechanics.
- Testing and Iteration: Test your prototypes with a small group of players. Gather feedback on clarity, difficulty, and engagement. Revise your puzzles based on this feedback, iterating until you achieve the desired balance of challenge and satisfaction. This iterative process is vital for refining puzzle design.
- Integration and Refinement: Once you are satisfied with the individual puzzles, integrate them into the overall escape room narrative. Ensure a smooth flow between puzzles and a logical progression of the story.
- Final Testing and Launch: Conduct thorough final testing with a wider range of players to identify any remaining issues. Make any necessary adjustments before launching your escape room.
Escape Room Puzzle Technology Integration
Escape room technology has evolved significantly, transforming simple lock-and-key puzzles into immersive, interactive experiences. Integrating technology not only adds complexity and excitement but also allows for more intricate storytelling and personalized gameplay. The right technology can elevate a puzzle from a simple challenge to a truly memorable moment within the overall escape room narrative.
Technology Overview
Several technologies can enhance escape room puzzles, each offering unique capabilities and challenges. These range from simple mechanical solutions to sophisticated electronic systems. The choice depends heavily on budget, desired complexity, and the overall theme and design of the escape room.
Technology Comparison
The following table compares several common technologies used in escape room puzzle design. Costs are estimates and can vary significantly based on specific components and vendor. Complexity reflects the difficulty of implementation and maintenance.
| Technology | Cost (USD) | Complexity | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple Mechanical Locks | $10 – $100 | Low | Affordable, reliable, easily accessible. |
| Magnetic Locks/Latches | $20 – $200 | Low to Medium | Clean integration, versatile, relatively inexpensive. |
| RFID Systems | $50 – $500+ | Medium | Allows for contactless interaction, trackable progress, can trigger multiple events. |
| Microcontrollers (Arduino, Raspberry Pi) | $20 – $200+ | Medium to High | Highly customizable, allows for complex logic and interactions, can integrate various sensors. |
| Hidden Compartments & Mechanisms | Variable, depending on complexity | Low to High | Adds an element of surprise and discovery; can be used with other technologies. |
Integrating RFID Technology into an Existing Puzzle
Let’s consider integrating an RFID system into a puzzle that currently uses a simple combination lock. The combination lock could be replaced with a small RFID reader. The solution to the puzzle would now involve finding a specific RFID tag, which, when scanned, unlocks an electronic latch. This requires replacing the lock mechanism with the RFID reader and programming the reader to trigger the latch release when the correct tag is presented.
Wiring and potentially a small power source would need to be discreetly incorporated into the puzzle’s design. The existing puzzle’s physical components might need minor adjustments for the RFID reader’s integration.
Creating a Puzzle Using Microcontrollers
A puzzle using a microcontroller could involve a series of illuminated buttons that need to be pressed in a specific sequence to unlock a box. An Arduino microcontroller could be programmed to monitor the button presses. Each button would be connected to a digital input pin on the Arduino. The code would track the order and timing of the presses.
If the sequence is correct, the Arduino would activate a relay, which in turn unlocks a solenoid-based lock on the box. A visual cue, such as a changing light pattern, could provide feedback to the players. The complexity of the sequence and the addition of timing elements or other sensors could increase the puzzle’s difficulty. For example, the sequence could be hidden within a cryptic clue or revealed through another puzzle within the room.
The Business of Escape Rooms and Puzzles

The escape room industry, a thrilling blend of entertainment and puzzle-solving, has experienced significant growth in recent years. However, success in this competitive market requires a keen understanding of business trends, effective marketing strategies, and a robust operational model. This section delves into the crucial business aspects of running a successful escape room.
Market Trends and Challenges
The escape room market is dynamic, constantly evolving to meet changing consumer preferences. Current trends include the rise of immersive and technologically advanced experiences, the incorporation of virtual reality elements, and a growing demand for themed rooms that cater to specific interests, such as horror, mystery, or fantasy. Challenges include managing operational costs, attracting and retaining customers in a saturated market, and adapting to evolving technological advancements.
Competition is fierce, requiring businesses to constantly innovate and offer unique experiences to stay ahead. The impact of economic downturns and seasonal fluctuations also presents a significant challenge, necessitating flexible pricing strategies and targeted marketing campaigns. For example, a smaller, independent escape room might struggle to compete with a large franchise that can leverage economies of scale and brand recognition.
Marketing and Customer Experience
Effective marketing is paramount for attracting customers and building brand loyalty. A comprehensive marketing plan should include a strong online presence through a professional website and social media engagement. Targeted advertising on platforms frequented by the target demographic is essential. Furthermore, building positive word-of-mouth marketing through exceptional customer service is crucial. A memorable and positive customer experience, from booking to the post-game interaction, significantly impacts customer satisfaction and repeat business.
This includes creating a welcoming atmosphere, providing clear instructions, and offering excellent customer service. For instance, offering discount codes or loyalty programs can incentivize repeat visits and referrals.
Business Models: Franchising versus Independent Operations
Escape room businesses operate under various models, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Franchising offers the benefit of established branding, marketing support, and operational systems. However, it typically involves significant upfront costs and ongoing royalty payments. Independent operations provide greater flexibility and control but require more investment in marketing and brand building. Independent operators often focus on creating unique, niche experiences to stand out from larger chains.
A franchise, on the other hand, can leverage the brand’s reputation and marketing power to attract a wider customer base. The choice between these models depends on factors such as financial resources, risk tolerance, and entrepreneurial vision.
Marketing Plan for a New Escape Room
This plan targets young adults (18-35) and families with older children (10+), drawn to mystery and adventure. Marketing channels include social media marketing (Instagram, Facebook, TikTok) focusing on visually appealing content showcasing room themes and puzzles. Local partnerships with tourism agencies and event planners are vital. A modest budget of $5,000 is allocated, with $2,000 for social media advertising, $1,500 for website development and maintenance, and $1,500 for local partnerships and promotional materials.
This plan emphasizes building online engagement through contests, user-generated content campaigns, and influencer collaborations. Pre-opening buzz will be generated through press releases and local media outreach. Post-launch, customer reviews and testimonials will be actively solicited and promoted. The goal is to achieve high customer satisfaction leading to strong word-of-mouth marketing.
Online Game Development and Escape Room Puzzles
The principles of compelling escape room design translate surprisingly well into the digital realm, offering a unique blend of puzzle-solving, narrative immersion, and collaborative gameplay. By leveraging the strengths of online platforms, developers can create engaging experiences that capture the essence of physical escape rooms while expanding their potential reach and interactivity.
Escape room puzzle design prioritizes logical progression, thematic consistency, and a satisfying sense of accomplishment. These elements are equally crucial in online game development. Well-designed puzzles should present a clear challenge, offer hints without giving away the solution, and ultimately reward players with a feeling of intellectual triumph. Furthermore, the narrative context of the puzzle should be integrated seamlessly into the game’s overall story, creating a cohesive and immersive experience.
Examples of Online Games Incorporating Escape Room-Style Puzzles
Several successful online games have expertly integrated escape room mechanics. Games like “The Room” series on mobile platforms offer intricate, physics-based puzzles within a captivating narrative framework. The puzzles require observation, manipulation of objects, and logical deduction, closely mirroring the experience of a physical escape room. Another example is “The Witness,” a first-person exploration game that features a wide array of environmental puzzles requiring spatial reasoning and pattern recognition.
These puzzles, while not explicitly presented as an “escape room,” share the core principles of logical progression and satisfying problem-solving. Furthermore, many online adventure games, particularly those with point-and-click interfaces, frequently incorporate puzzle elements that require players to examine their environment, interact with objects, and solve riddles – key components of a well-designed escape room.
Concept for an Online Escape Room Game: “The Chronarium Heist”
“The Chronarium Heist” is a collaborative online escape room game set within a fictional museum housing a collection of historical artifacts. Players, acting as a team of expert thieves, must infiltrate the museum after hours to steal a powerful artifact – a time-altering device known as the Chronarium. The game features a branching narrative, with player choices impacting the difficulty and outcome of the experience.
Gameplay mechanics involve navigating a 3D rendered museum environment, interacting with objects using a point-and-click interface, solving puzzles that integrate elements of code-breaking, historical trivia, and logic puzzles. The puzzles are designed to be solvable collaboratively, requiring players to share information and combine their skills. For example, one puzzle might involve deciphering a coded message found in a historical document, while another might require manipulating clockwork mechanisms to unlock a hidden passage.
The game incorporates a timer to add a sense of urgency and challenge, and a hint system is available to assist players without completely revealing the solutions. The game will also feature a variety of difficulty settings to cater to different skill levels.
Challenges of Translating the Physical Escape Room Experience to a Digital Environment
Translating the tactile and physical aspects of an escape room to a digital environment presents several unique challenges. The sense of physical presence and interaction with tangible objects is difficult to replicate fully. Creating an intuitive and engaging user interface for interacting with virtual objects is crucial. Furthermore, preventing players from resorting to exploits or unintended solutions requires careful game design and testing.
Maintaining the immersive atmosphere and creating a sense of urgency and suspense within a digital environment also requires careful consideration of visual design, sound design, and narrative pacing. The absence of direct physical interaction with puzzles necessitates a reliance on clever visual cues and intuitive game mechanics to guide players. Finally, effectively recreating the collaborative aspect of a physical escape room requires well-designed communication tools and a game structure that encourages teamwork and shared problem-solving.
Related Game Genres and Puzzle Elements
Escape rooms, while a unique experience, share a surprising amount of DNA with other game genres. The core element – solving puzzles to achieve a goal – is a fundamental building block across many forms of interactive entertainment. Examining these shared elements and their differences illuminates the specific strengths and challenges of escape room design.
The similarities and differences between escape room puzzles and those in other genres are fascinating. While online game development, online driving and racing games may seem worlds apart from a physical escape room, the underlying principles of puzzle design and player engagement often overlap significantly. This comparison reveals the broader spectrum of puzzle mechanics and player experiences across diverse gaming platforms.
Similarities and Differences in Puzzle Design Across Game Genres
Escape room puzzles often rely on a combination of logic, observation, and physical manipulation. Online games, in contrast, primarily use digital interfaces, limiting physical interaction. However, both share common puzzle elements like riddles, codes, and sequence puzzles. Online driving and racing games, while seemingly action-focused, frequently incorporate puzzle elements such as navigating complex routes, solving timing challenges, or utilizing specific vehicle upgrades strategically.
The key difference lies in the level of physical interaction and the context in which puzzles are presented. Escape rooms immerse players physically, while digital games offer a more abstract, screen-mediated experience.
Common Puzzle Elements Across Game Genres
A surprising number of puzzle elements transcend genre boundaries. Many puzzles rely on fundamental logical principles, regardless of the platform.
The following list details common puzzle elements and their variations across genres:
- Logic Puzzles: These are found everywhere, from Sudoku in mobile games to complex deduction challenges in escape rooms and mystery-solving online games. Variations include pattern recognition, spatial reasoning, and numerical sequences.
- Code Breaking: Cipher puzzles appear in many games, ranging from simple substitution ciphers in escape rooms to complex encryption challenges in online strategy games. The complexity and context vary widely.
- Inventory Puzzles: Combining items to solve a problem is common in adventure games, escape rooms, and even some racing games (finding specific upgrades to improve performance). The context shifts, but the core mechanic remains consistent.
- Riddle Solving: Word puzzles and riddles appear frequently across genres. Their complexity ranges from simple wordplay to intricate, multi-layered riddles.
Player Experience Comparison
The player experience differs significantly across genres. Escape rooms provide a fully immersive, collaborative, and physically interactive experience. The sense of urgency and shared problem-solving adds a layer of excitement unique to this genre. Online games offer a more individualized experience, often with a wider range of difficulty levels and replayability. Online driving and racing games focus on skill and reflexes, with puzzles often integrated into the core gameplay loop, such as navigating a challenging track or mastering a specific driving technique.
Examples of Puzzles from Various Game Genres
The following examples illustrate the diversity of puzzle mechanics and difficulty levels across different game genres:
- Escape Room (Easy): A combination lock requiring a three-digit code found hidden within a book. (Mechanic: Code Breaking; Difficulty: Easy)
- Escape Room (Hard): A complex series of interconnected puzzles requiring the solution of a cryptic riddle, a geometric puzzle, and a cipher to unlock a final combination lock. (Mechanic: Multi-stage puzzle; Difficulty: Hard)
- Online Puzzle Game (Medium): A Sudoku puzzle with increasing difficulty levels. (Mechanic: Logic Puzzle; Difficulty: Medium)
- Online Driving Game (Easy): Navigating a simple track within a time limit. (Mechanic: Timing Challenge; Difficulty: Easy)
- Online Racing Game (Hard): Mastering a challenging track with tight corners and obstacles while managing fuel and tire wear. (Mechanic: Skill-based challenge with strategic elements; Difficulty: Hard)
Gambling and Game Design Considerations (Ethical Considerations)
Integrating gambling mechanics into games presents a complex ethical landscape, demanding careful consideration of player welfare and legal compliance. The allure of chance and reward can be incredibly engaging, but it also carries the potential for harm if not handled responsibly. This section explores the ethical considerations, legal frameworks, and design approaches involved in incorporating gambling elements into games, particularly within the context of escape rooms.
Ethical Considerations in Game Design with Gambling Mechanics
The primary ethical concern revolves around preventing gambling addiction and protecting vulnerable players. Games should be designed to minimize the risk of harmful gambling behavior. This includes implementing robust responsible gaming features such as deposit limits, time limits, and self-exclusion options. Clear and accessible information about the odds and potential risks associated with gambling mechanics must be provided.
Furthermore, the game’s overall tone and presentation should avoid glorifying or romanticizing gambling. The focus should remain on the core game experience, with gambling elements serving as a supplementary feature, not the central attraction. Games should avoid manipulative techniques designed to encourage excessive spending or playing time. Consideration should be given to the player’s age and psychological profile.
Legal Frameworks and Regulations Surrounding Online Gambling
The legal landscape surrounding online gambling varies significantly across jurisdictions. Many countries have strict regulations governing online gambling, including licensing requirements, taxation, and restrictions on advertising. Developers must thoroughly research and comply with the relevant laws in each region where their game will be distributed. Failure to comply can result in severe penalties, including fines and legal action.
Key aspects of these regulations often include: age verification systems to prevent underage gambling, measures to prevent money laundering, and mechanisms for handling disputes and player complaints. For example, in the UK, the Gambling Commission sets stringent standards for online gambling operators, requiring robust player protection measures and regular audits. In contrast, some jurisdictions may have more lenient regulations or even outright prohibitions on online gambling.
Design Approaches: Games with and without Gambling Elements
Games without gambling elements typically focus on skill, strategy, and problem-solving. The player’s progression is determined by their ability to overcome challenges and master the game mechanics. In contrast, games with gambling elements introduce an element of chance, where outcomes are partially determined by random events. The design approaches differ significantly. Games without gambling elements often prioritize a balanced and fair gameplay experience, ensuring that player skill is the primary determinant of success.
Games with gambling elements, however, must carefully balance the thrill of chance with the risk of loss, employing responsible gaming features to mitigate potential harm. For instance, a purely skill-based escape room might involve solving complex puzzles, while a variation incorporating gambling could involve wagering virtual currency on the outcome of a mini-game within the escape room scenario, with clear odds and limitations in place.
Potential Risks and Benefits of Integrating Gambling Features
Integrating gambling features can increase player engagement and monetization potential. The thrill of chance and the possibility of winning rewards can be highly motivating. However, this comes with the risk of fostering addictive behavior and causing financial harm to players. The benefits must be carefully weighed against the potential negative consequences. Responsible game design is crucial to mitigate these risks.
For example, the integration of gambling chips in an escape room could provide an added layer of challenge and reward, but only if strict limits are implemented on the amount that can be wagered and the overall impact on the gameplay is minimal, ensuring the primary focus remains on puzzle-solving. Conversely, poorly implemented gambling features could lead to frustration, financial losses, and even addiction, ultimately harming the player experience and the reputation of the game.
Gambling Industry and Career Paths
The gambling industry, encompassing casinos, online platforms, lotteries, and related businesses, offers a diverse range of career opportunities beyond just dealing cards or spinning roulette wheels. From regulatory oversight to technological innovation, numerous roles require specialized skills and expertise, contributing to the industry’s complex operations and global reach. Understanding the various career paths and their requirements is crucial for anyone considering a future in this dynamic sector.
Career Opportunities within the Gambling Industry
The gambling industry employs professionals across various disciplines, including finance, technology, law, marketing, and operations. Regulatory bodies, such as gambling commissions, also provide essential oversight and enforcement, ensuring fair play and responsible gaming practices. Specific roles range from casino dealers and pit managers to software developers, data analysts, compliance officers, and marketing specialists. Gambling commissions themselves employ investigators, auditors, licensing specialists, and legal professionals to regulate the industry effectively.
Skills and Qualifications Required for Gambling Industry Roles
The skills and qualifications needed vary significantly depending on the specific role. For example, a casino dealer requires excellent interpersonal skills, knowledge of specific games, and the ability to handle cash transactions accurately. A software developer in the online gaming sector needs strong programming skills and experience in relevant technologies. Compliance officers must possess a deep understanding of relevant regulations and legislation, while marketing professionals need creative thinking and strategic planning abilities.
Many roles benefit from a strong understanding of statistics and probability. Formal education, such as a degree in a relevant field, is often beneficial, but practical experience and professional certifications can also be highly valuable.
Work Environments and Salary Expectations
Work environments differ greatly across the gambling industry. Casino roles often involve shift work, evenings, and weekends, in a fast-paced and high-pressure environment. Online gaming roles might offer more flexible hours and a less demanding atmosphere. Regulatory positions within gambling commissions typically involve office-based work with a focus on compliance and enforcement. Salary expectations vary considerably based on experience, location, and role.
Entry-level positions may offer competitive salaries, while senior management and specialized roles can command significantly higher incomes. Location also plays a crucial role, with major gambling hubs often offering higher compensation packages. For example, a senior software engineer in Las Vegas might earn considerably more than a similar role in a smaller city.
Career Path Guide for the Gambling Industry
A career in the gambling industry can be pursued through various educational pathways. A bachelor’s degree in business administration, computer science, law, or a related field can provide a strong foundation. Further specialization can be achieved through postgraduate studies or professional certifications. Networking within the industry, through internships, conferences, and professional organizations, is vital for career advancement.
Continuous professional development, including staying abreast of technological advancements and regulatory changes, is crucial for long-term success. For example, someone interested in a compliance role might pursue a relevant certification, while an aspiring data analyst might focus on acquiring expertise in data visualization and machine learning techniques.
Gambling’s Geographic Impact
The rise of gambling, both in physical casinos and the burgeoning online realm, has profoundly reshaped the economic and social landscapes of numerous cities and countries. This impact is multifaceted, presenting both significant opportunities and considerable challenges for communities and their governance. Understanding this geographic impact requires examining the economic benefits and drawbacks, contrasting regulatory approaches, and considering the social consequences that ripple through affected populations.Gambling Cities and Their Economic ImpactGambling cities, often strategically located for tourism and accessibility, experience a surge in revenue from casinos, hotels, restaurants, and ancillary businesses.
Las Vegas, Macau, and Monte Carlo serve as prime examples, where the gambling industry fuels significant employment, attracts substantial investment, and generates substantial tax revenue for local governments. However, this economic boon is often accompanied by increased costs in infrastructure development, social services, and law enforcement to manage the influx of people and the potential for associated crime.
Furthermore, the concentration of wealth generated by casinos doesn’t always translate into equitable distribution within the community, potentially exacerbating existing inequalities.Social and Economic Consequences of GamblingThe social and economic consequences of gambling are complex and often intertwined. Positive impacts can include increased tourism, job creation, and tax revenue contributing to public services. However, negative consequences are equally significant and include problem gambling addiction, which can lead to financial ruin, family breakdown, and mental health issues.
The rise of online gambling has further complicated this issue, making access to gambling readily available and potentially increasing the risk of addiction for vulnerable populations. Moreover, the potential for money laundering and organized crime associated with gambling operations poses a significant threat to social stability and economic security.Regulatory Approaches to Gambling: A Global ComparisonDifferent jurisdictions adopt vastly different approaches to regulating gambling.
Some, like the United Kingdom, have a relatively liberalized approach with extensive licensing and oversight, while others, such as many countries in the Middle East, maintain strict prohibitions. The regulatory landscape in the United States is particularly varied, with individual states possessing significant autonomy in determining the legality and regulation of gambling within their borders. This patchwork approach leads to a complex interplay of legal frameworks and enforcement challenges.
The regulatory strategies employed often reflect cultural attitudes towards gambling, economic priorities, and the perceived social costs associated with the industry.Gambling Regulation Comparison: Key Features
| City/Country | Legalization Status | Regulation Type | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Las Vegas, USA | Legalized and heavily regulated | State-level regulation | Strict licensing, taxation, and anti-money laundering measures; robust consumer protection initiatives are in place, though enforcement varies. |
| Macau, China | Legalized and heavily regulated | Central government regulation | High taxation rates, strict licensing requirements, and emphasis on controlling the flow of capital. Focus on preventing crime and corruption. |
| Singapore | Legalized and strictly regulated | National-level regulation | Stringent entry restrictions, high taxation, and measures aimed at minimizing problem gambling. A significant portion of revenue is channeled to social programs. |
| United Kingdom | Legalized and regulated | National-level regulation | Licensing of operators, advertising restrictions, and measures to promote responsible gambling. Significant focus on player protection. |
Conclusion
So, whether you’re designing your own escape room, planning a visit to one, or simply curious about the magic behind these immersive experiences, we hope this exploration has sparked your interest. The world of escape rooms is a dynamic blend of creativity, technology, and business acumen, constantly evolving with new challenges and innovative solutions. The escape room puzzle isn’t just a game; it’s a testament to human ingenuity and the enduring appeal of a good mystery.
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes a good escape room puzzle?
A good escape room puzzle is well-themed, intuitive (not overly obscure), solvable with logic and observation, and provides a satisfying “aha!” moment upon completion. It should also be appropriately challenging for the target audience.
How much does it cost to build an escape room?
Costs vary wildly depending on size, complexity, technology used, and location. Expect a range from a few thousand to tens of thousands of dollars.
What are some common escape room puzzle themes?
Popular themes include mystery, horror, fantasy, sci-fi, history, and even pop culture references. The possibilities are virtually endless!
How long does it take to design an escape room puzzle?
This depends on complexity, but expect to spend several hours to weeks per puzzle, including design, testing, and refinement.